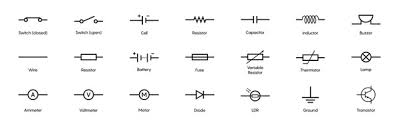
For anyone new to the world of electrical and electronics, it can often feel like there is an overwhelming amount of terminology and components to understand. From basic circuits to advanced semiconductor devices, getting a solid foundation is essential for progressing in the field. This guide will take you through the top 20 key terms and devices, providing a simple and clear explanation of each one to help you get started.
1. Open Circuit
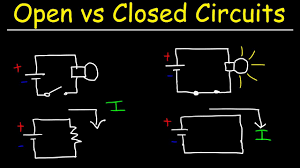
An open circuit occurs when there is a break in the path of an electrical circuit, preventing current from flowing. It is essentially an incomplete circuit, meaning no electricity can travel from the power source to the load (like a light bulb or motor).
2. Short Circuit
A short circuit happens when an unintended low-resistance path allows excessive current to flow. This usually occurs when two wires touch, bypassing the load and causing a potentially dangerous increase in current. Short circuits can cause overheating, damage to components, or even fires.
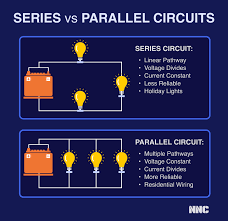
3. Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit, multiple components are connected side by side, each having its own path to the power source. This means if one component fails, the others can still function. Parallel circuits are commonly used in household wiring systems where different appliances operate independently.
4. Series Circuit
In a series circuit, components are connected one after the other in a single path. The current flows through each component in turn. If one component fails, the entire circuit is broken. A good example is older string lights for holiday decorations—if one bulb goes out, they all do.
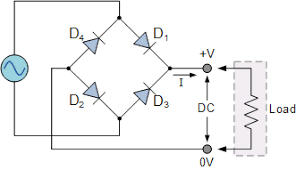
5. Bridge Rectifier
A bridge rectifier is a type of circuit that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It is made up of four diodes arranged in a “bridge” configuration. This is commonly used in power supply circuits to provide DC voltage from an AC source.
6. LED (Light Emitting Diode)
LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electrical current flows through them. They are highly energy-efficient and are used in everything from indicator lights to large display screens. LEDs are favored for their low power consumption and long lifespan.
7. Switch
A switch is a simple device used to control the flow of electrical current in a circuit. When the switch is “on,” it closes the circuit, allowing current to flow. When it is “off,” it opens the circuit, stopping the current. Switches come in various forms such as toggle switches, push-button switches, and slide switches.
8. Battery
A battery is a device that stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy to power circuits. Batteries have two terminals: positive and negative. They come in many forms, such as disposable alkaline batteries and rechargeable lithium-ion batteries used in smartphones and laptops.
9. MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor)
A MOSFET is a type of transistor used for switching and amplifying signals in electronic devices. It is widely used in power electronics due to its high efficiency and fast switching speed. MOSFETs are commonly found in switching power supplies and motor control circuits.

10. BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor)
A BJT is another type of transistor that controls current flow. It has three layers and two junctions, making it slightly different from MOSFETs. BJTs are commonly used for amplification and switching. The two main types of BJTs are NPN and PNP, named after the arrangement of their semiconductor layers.
11. Resistor
Resistors are passive components that limit the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are used to control voltages and currents to protect other components. Resistors are rated by their resistance value, measured in ohms (Ω), and their power rating, measured in watts (W).
12. Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores and releases electrical energy. It is made of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material. Capacitors are used in many applications, such as filtering signals, stabilizing power supplies, and for timing circuits. The unit of capacitance is the farad (F).
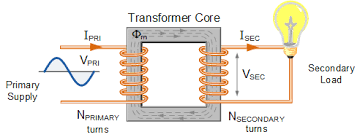
13. Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It is primarily used to step up (increase) or step down (decrease) voltage levels. Transformers are essential in power transmission systems for distributing electricity over long distances.
14. Inductor
An inductor is a passive component that stores energy in a magnetic field when current flows through it. Inductors are commonly used in filters, transformers, and to manage high-frequency signals in electronic circuits. Its unit is the henry (H).

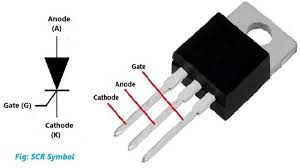
15. SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier)
An SCR is a type of semiconductor device used as a switch to control high voltages and currents. It only conducts when a gate signal is applied, making it useful for controlling power in devices like motor drives, heaters, and lighting systems.
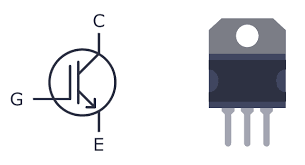
16. IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor)
IGBTs combine the best features of BJTs and MOSFETs. They are used in high-power applications like electric cars and industrial equipment, where high efficiency and fast switching are required.
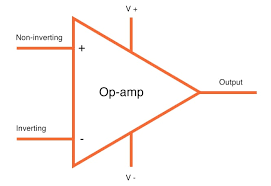
17. Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp)
An op-amp is a high-gain voltage amplifier with differential input and single-ended output. It is used in many applications, including signal conditioning, filtering, and analog computing. A popular configuration of the op-amp is the comparator, where it compares two voltages and outputs a high or low signal depending on the comparison.
18. Comparator
A comparator is a specialized op-amp that compares two input voltages and outputs a digital signal based on which input is higher. Comparators are commonly used in zero-crossing detectors, oscillators, and voltage-level detection circuits.
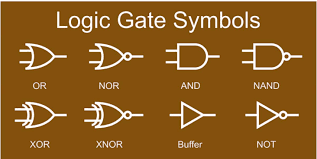
19. Logic Gates
Logic gates are the building blocks of digital circuits. They perform basic logical functions (AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR) by outputting a specific result based on binary input signals (0s and 1s). Logic gates are fundamental in processors, memory devices, and other digital systems.
20. Diodes and Their Types
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only. Diodes are used for rectification, voltage regulation, and protection. There are several types of diodes:
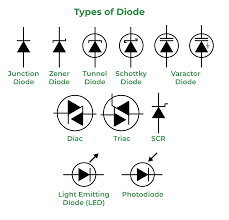
- Standard Diode: Used in rectification circuits to convert AC to DC.
- Zener Diode: Allows current to flow in reverse when a certain voltage is reached, often used for voltage regulation.
- Schottky Diode: Has low forward voltage drop and fast switching, used in high-speed circuits.
- Light Emitting Diode (LED): Emits light when forward biased.
- Photodiode: Converts light into current, commonly used in sensors.
Conclusion
Understanding these essential terms and devices is the first step toward mastering electrical and electronics concepts. Whether you’re working with simple circuits or complex electronic systems, having a strong grasp of these components will help you design, troubleshoot, and innovate. For beginners, focusing on the practical applications of each device can also provide insight into how they fit together in larger systems.